by Teoman Erönü
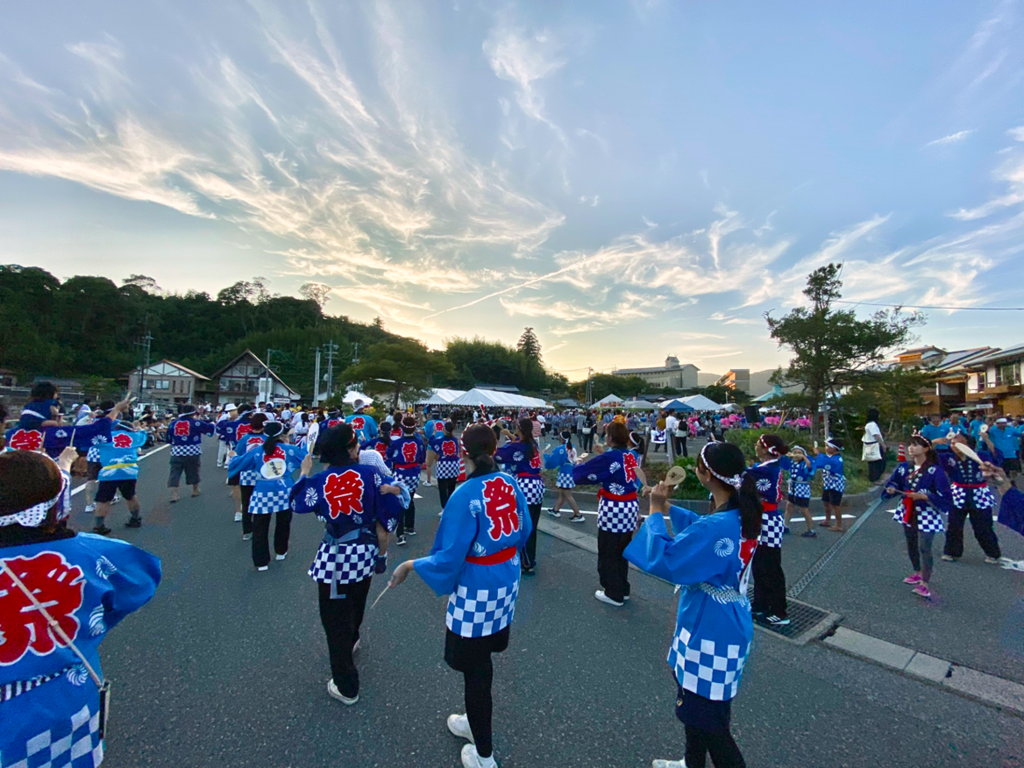
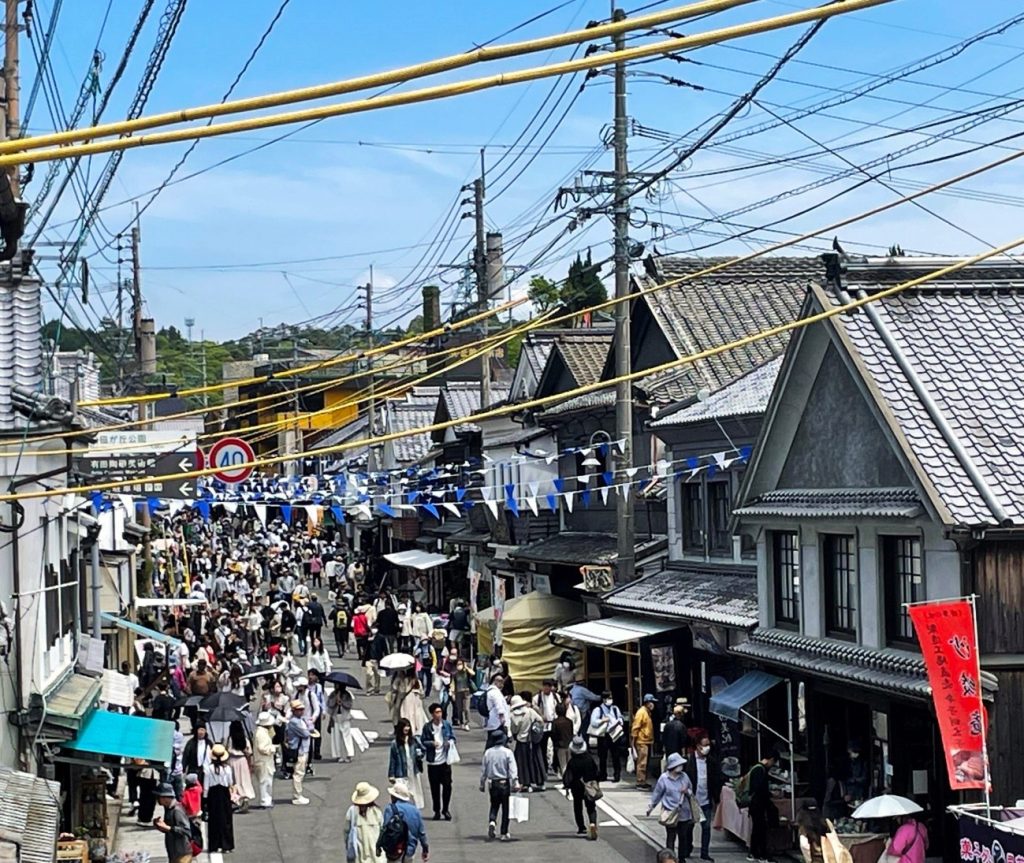
Porcelain has been one of the most important features of Arita’s local identity since the discovery of porcelain stone in the Izumiyama quarry in 1616. In that year, Korean potter Lee Sampyeon (Ri San Pei in Japanese) found kaolin and porcelain was made in Japan for the first time. After this discovery, craftsmen and artists continued porcelain production over the course of more than 400 years. However, as mentioned in previous articles on this blog, many of the local kilns have had to close as demand for the ‘white gold’ has declined since the 1990s and it has become increasingly difficult to find young people to carry on this legacy. Local festivals such as the Arita Porcelain Fair in spring preserve the town’s traditions and, with over a million visitors a year, are one of the few remaining signs of life of the small town’s once thriving industry.

Copyright © Arita Tourism Association 2023
This fact is palpable in the local community, as several groups and individuals, including the city’s mayor, Matsuo Yoshiaki, and Arita City Hall, are doing their best to revitalize this core industry with PR and advertising campaigns as well as international partnership initiatives such as the Creative Residency Arita project. Another important partnership I would like to introduce is the city’s partnership with the German “porcelain city” of Meissen. Meissen was the first European city where porcelain was produced after Friedrich Böttger’s discoveries in 1710, and has also developed a local identity centered around porcelain production. This led to both cities signing a city partnership agreement on February 9, 1979 and thus becoming twin cities. Since then, the two towns have grown closer and closer and have maintained their shared local identity through reciprocal visits by delegations from the two towns at local celebrations. The local Arita-Meissen Friendship Association also plays an important role in connecting the two cities, as it has been organizing youth exchanges between the two cities since 1994.

Copyright © Arita Tourism Association 2022
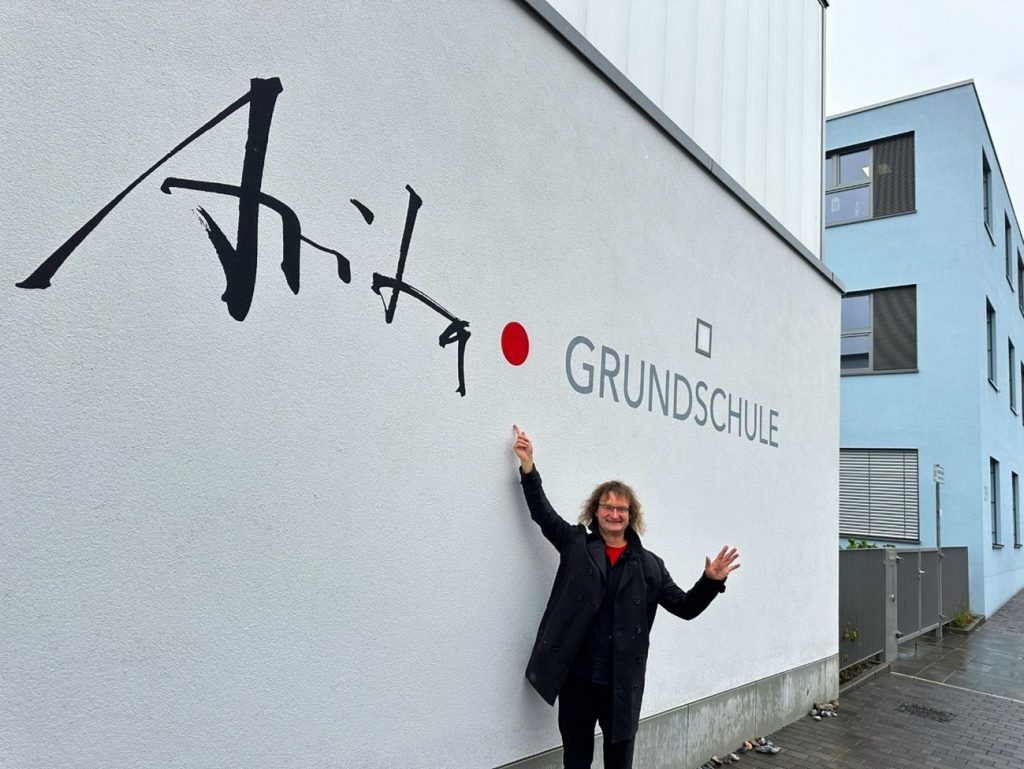
A new cooperation is planned for 2024, as an elementary school in Meissen, which has renamed itself “Arita Elementary School Meissen”, has proposed a partnership with Arita Elementary School in Arita. Educating the children about their respective histories and similarities through cultural exchange projects is an attempt to raise awareness of the role of porcelain in the minds of children in both cities. The Japanese children proudly presenting their porcelain to the German children during an online exchange project and talking about the pottery lessons in their school is just one of many expressions of these efforts. 2024 marks the 45th anniversary of signing the twin city agreement between Arita and Meissen, and the partnership between the two schools will be officially sealed during an official visit by the principal of “Arita Elementary School Meissen” to Arita. On this occasion, a revival of the local youth exchange, which had been interrupted due to the Covid pandemic, is also planned.

Copyright © Gaby Bachmann 2023
The efforts of the city of Meissen do not stop here. Together with the “State Porcelain Manufactory”, the “Meissen Porcelain Foundation” and the state-owned company “State Palaces, Castles and Gardens of Saxony”, the city has applied to be included on the UNESCO World Heritage List. However, after this application was rejected at the most recent special meeting of the Ministry of Culture on December 4, 2023, the Mayor of Meissen, Olaf Raschke, announced in an interview that a joint application with the city of Arita is being considered, with the porcelain production of both cities being the focus of the application. A successful bid would not only deepen the connection between the two cities at a local level, but would of course also boost national and international tourism and be an important step towards revitalizing both cities. The talks will take place during the official visit of a delegation from Meissen to Arita in fall 2024 on the occasion of the 45th anniversary of the town twinning.
Teoman Erönü graduated from the BA program in Japanese Studies at Freie Universität Berlin in 2021. He is currently the Coordinator for International Relations (CIR) in Arita as part of the JET program.