by Lynn Ng
Digital technologies dominate a significant aspect of our daily lives, and, with infrastructural and regulatory support, hold tremendous potential in promoting Japan’s social and economic growth. Japan’s focus on improving its digital environment and governance is recently most evidenced by the nation’s well-reported organization of the Japan-EU Digital Partnership Council first held on 3 July 2023 [1]. With promises of strategic cooperation in research and development of 5G networks and digital trade principles, as well as data governance and cybersecurity, Japan (as well as the European Union) is arming itself with resources for the new digital society – or commonly referenced as “Society 5.0.”
Other preparations towards Society 5.0 include Prime Minster Fumio Kishida’s announcement of the “Vision for a Digital Garden City Nation” in 2022 [2], thereby kick-starting the rapid transformation particularly of Japan’s rural regions. Rural Japan’s digital transformation since the announcement is increasingly noticeable and has caught the attention of many contributors to this blog. Recent posts on this blog examine the emergence of smart farming, the development of digital human resources, and the potential of digital transformation in Japan’s regions. Followers of this blog would thus by now have a good grasp on what digitalization and digital transformation (DX) are, and what these keywords mean for Japan.

Copyright © Lynn Ng 2023
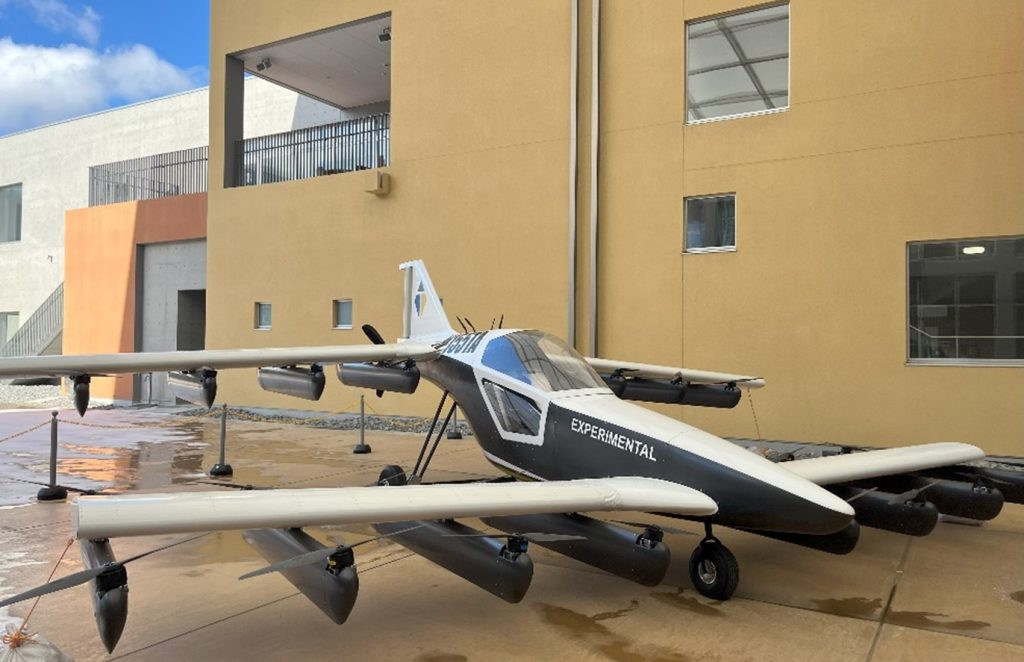
Fukushima is also well onto this trend. As a part of the “Vision for a Digital Garden City Nation,” cities in Fukushima prefecture host several technological and digital research facilities, one of them being the Robot Test Field (RTF) [3] in Namie-town – a town greatly affected by the nuclear disaster of 2011. RTF currently houses incredible facilities that support drones and other un-manned aerospace and deep-space, as well as underwater technological research, among many other cutting-edge technologies. RTF opened in March 2020 amidst the coronavirus pandemic. In January 2023, I visited the RTF facility and spoke with Mr. Sato, a middle-aged mechanical engineer and operations manager of the facility, about the former disaster region’s digital growth. We stood on the roof of the building, me shivering in mid-January chills, as Mr. Sato explains to me what research goes on in the different structures in the vicinity of the main building. Mr. Sato, a returnee to Namie-town, waves at the vast land earmarked for RTF developments that we stood on, and exclaimed how much the region has changed in the last two years.

Copyright © Lynn Ng 2023 and 2022
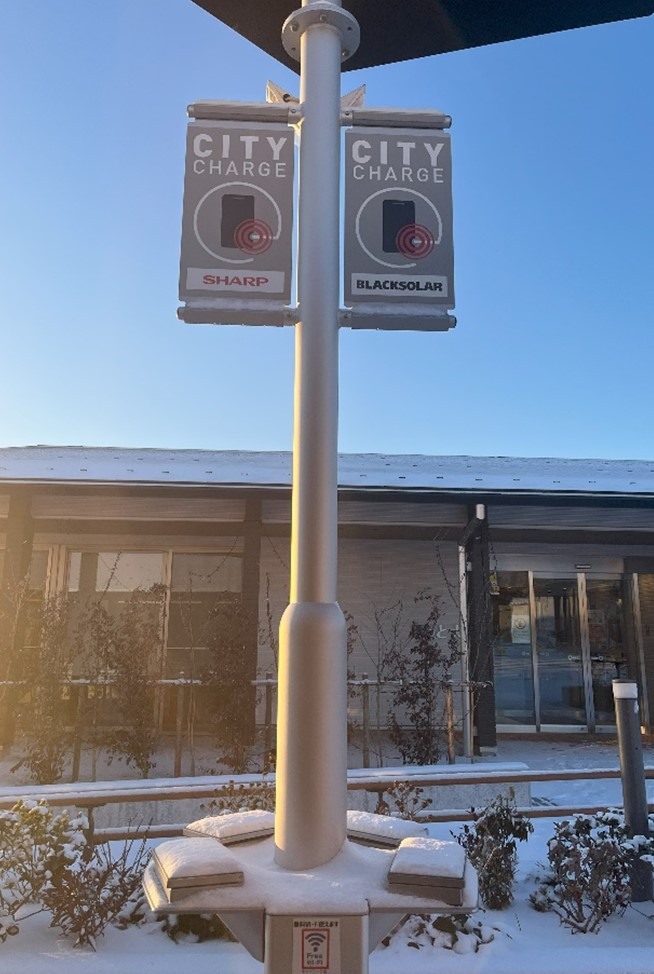
But the technological transformation of Fukushima goes beyond RTF. I encountered new technologies across Fukushima prefecture, such as un-manned convenience stores, automated lawnmowers, and drones. In Namie-town, I was taught by locals how to use the shiny display panels to call for on-demand free taxi services that run across the town [4]. In Okuma-town, I watched municipal officials grab sandwiches and snacks off a shelf that they smoothly paid for using a QR code. Perhaps none of these technologies are as advanced as the deep-space research going on within RTF, but the transformation in behavior is obvious. Locals use digital technologies in their everyday lives in many parts of Fukushima. I asked a municipal officer charging his mobile at one of the many public charging posts, to which he had simply replied: “Ah right, yeah. These are just everywhere here.” Digital transformation of Japan, and any other society, involve not only the establishment of infrastructure and research of new technologies and regulations, but also the uptake of these new technologies by the people. This seems to work well in Fukushima.
[1] Digital Agency. (2023). Japan-EU Digital Partnership Council held. Retrieved online: https://www.digital.go.jp/en/7faa668c-3787-4ff8-934b-093c4d2448c5-en#main-results
[2] JapanGOV. (2022). Vision for a Digital Garden City Nation: Achieving Rural-Urban Digital Integration and Transformation. Retrieved online: https://www.japan.go.jp/kizuna/2022/01/vision_for_a_digital_garden_city_nation.html
[3] FIPO. (2023). Fukushima Robot Test Field. Retrieved online: https://www.fipo.or.jp/robot/en/overview
[4] Nissan Smart Mobility. (2023). Smart Mobility in Namie. Retrieved online: https://www.smamobi.jp/






























